We use analytics and cookies to understand site traffic. Information about your use of our site is shared with Google for that purpose. Learn more.
Auditing and Logging
Introduction
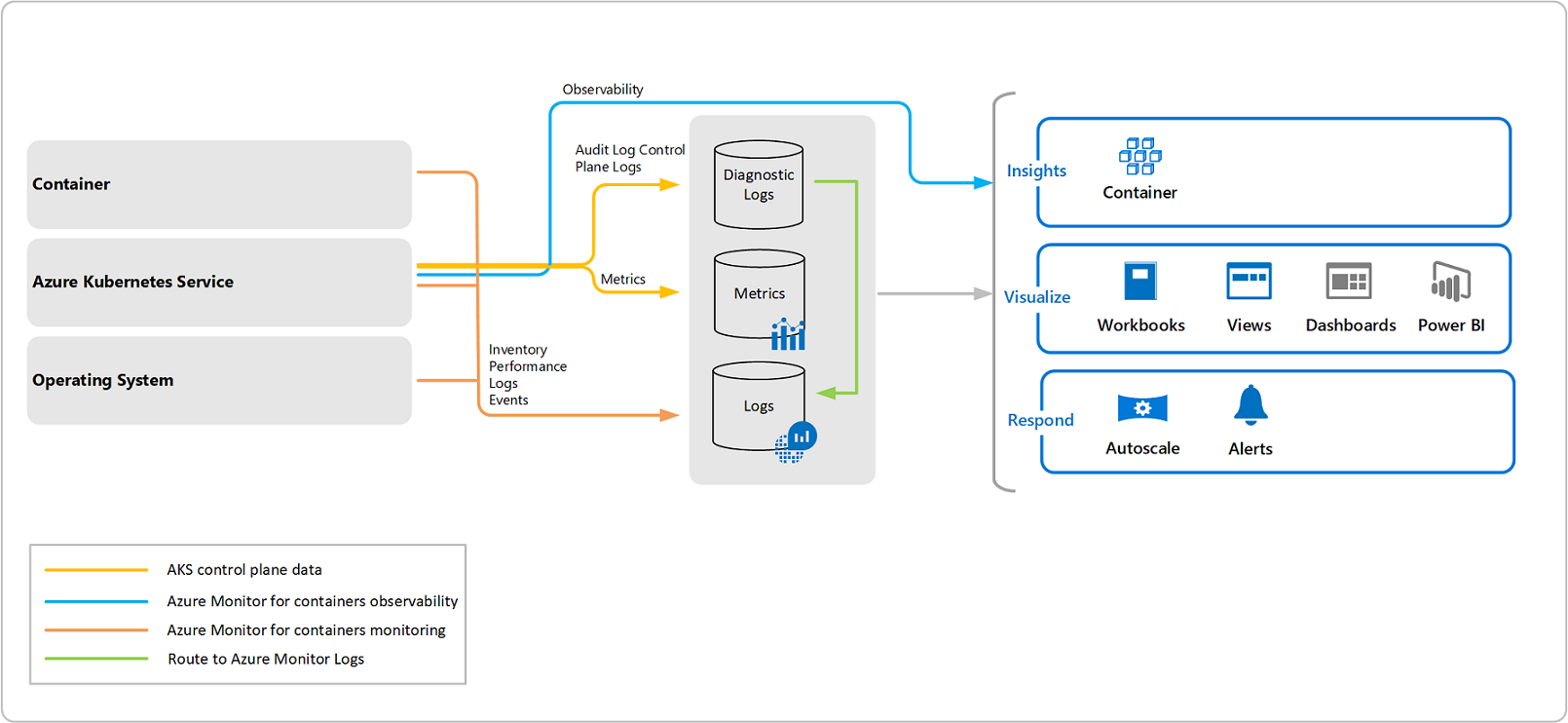
The Cloud Native platform on AKS continuously inventories all system components, monitors the performance and security of all components, and logs application and system events.
The process starts with application logging, compute resource monitoring, storage monitoring, network monitoring, security monitoring, and data monitoring at the Kubernetes pod level. Each application will need to determine how it is divided into subsystems, the number of subsystems, and the specific monitoring mechanisms within the subsystems. The security tools within each subsystem (e.g., the Sidecar Container Security Stack) will aggregate and forward the event logs gathered from monitoring to a locally centralized aggregated logs database on the platform.
It is important to highlight that this is entirely automated within the Kubernetes cluster. The aggregated logs will be further forwarded to the chosen cloud logging platform (Azure Log Analytics) after passing the program application configured log filter. The program’s local log analysis capability will analyze the aggregated logs and generate alerts and reports.
Created and Open Sourced Terraform modules:
- terraform-kubernetes-audit
- terraform-kubernetes-fluentd
- terraform-kubernetes-elastic-cloud
- terraform-kubernetes-prometheus
- terraform-kubernetes-istio-operator
Auditd will audit all of the container functionality.
Fluentd will collect all of the container logs.
Elasticsearch stores and search logs leveraging Kibana to visualize them.
Prometheus is used for real time metrics along with Alert manager to generate alerts and Grafana for visualizations.
Finally Istio will collect all of the network traffic send and recieved by the applications.
Centralized Logging Platform
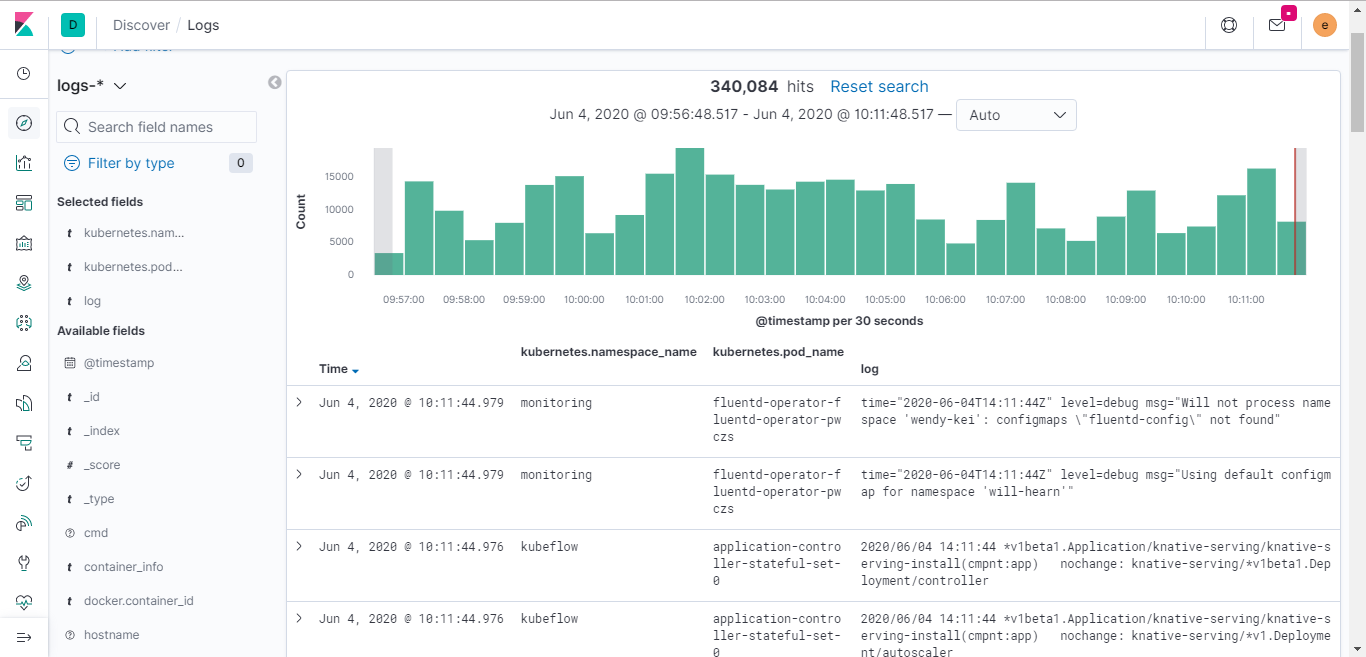
Once processed by the audit pipeline, all logs will be stored into an Elasticsearch environment. Elasticsearch is a search engine which functions well with log content. It also understands the fields in the audit log, allowing for dynamic querying against the entire audit log set.
Additionally, through Kibana (or other external tools), any report based on the audit logs can be generated. It is also possible to generate graphs or other visualizations to assist with investigation and/or anomaly detection.
For AKS-based clusters, audit logs are stored immediately offloaded and stored in an Azure Storage Account and then processed and sent into an Elasticsearch cluster by a specialized container running on the node.
For AKS-Engine based cluster, audit logs will be written onto the disk of the master nodes and then processed and sent into an Elasticsearch cluster by a specialized container running on the node.
Audit Logs
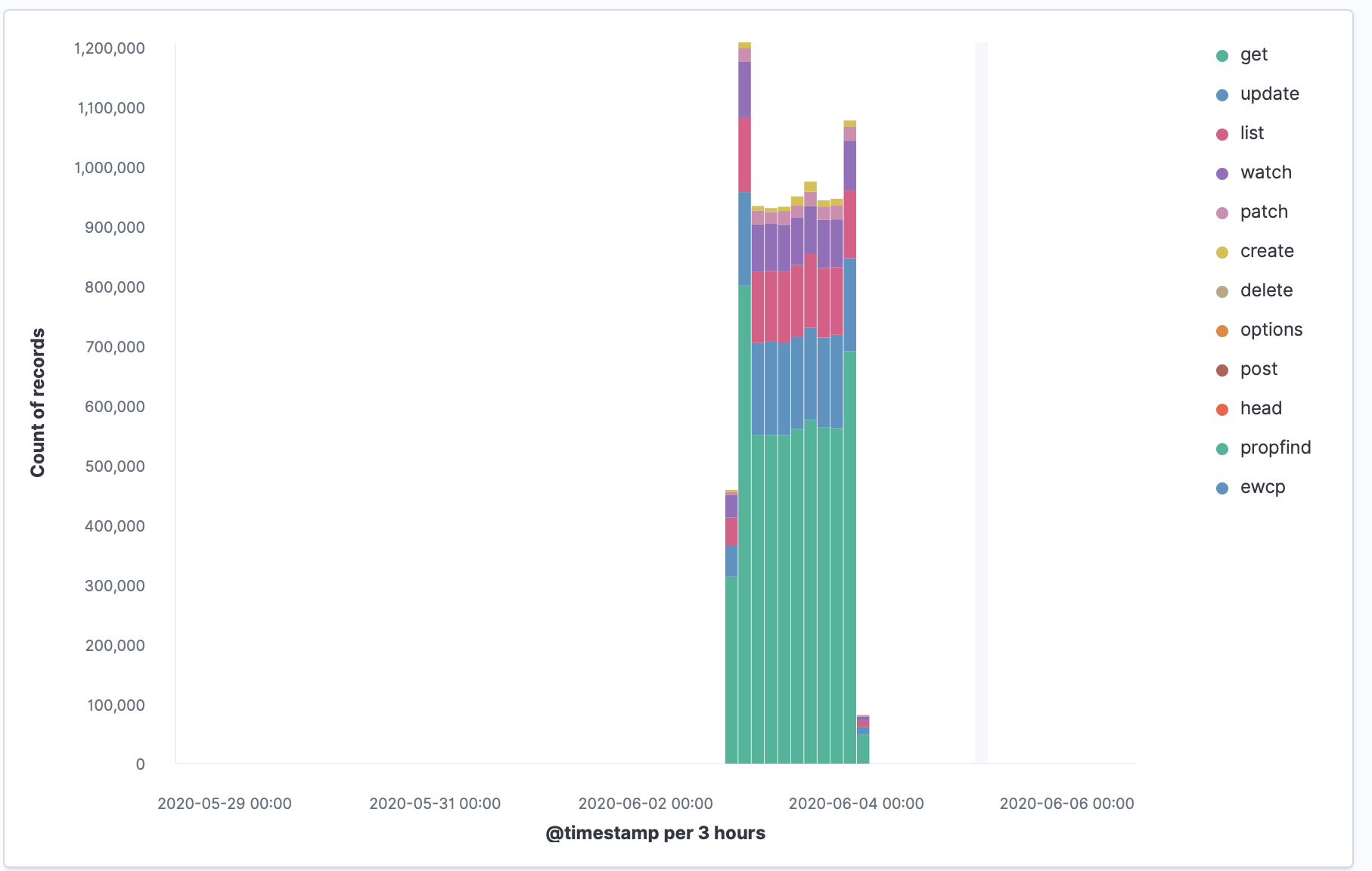
Kubernetes auditing provides a securityrelevant chronological set of records documenting the sequence of activities that have affected system by individual users, administrators or other components of the system.
Auditing logs required as part of any security audit process with internal or external process can be additionally sent to another system for further processing as required.
It allows cluster administrator to answer the following questions:
- what happened?
- when did it happen?
- who initiated it?
- on what did it happen?
- where was it observed?
- from where was it initiated?
- to where was it going?
Additionally here is the list of events for which an audit log will be generated:
- Creating a resource
- Updating a resource
- Deleting a resource
- Accessing a resource
- Access to a resource (e.g., port-forward or exec)
Audit Logs Content
At a minimmum, audit logs will contain the following information:
Audit Logs Retention
The Centralized Logging Platform will retain audit records for 6 months at a minimum in order to provide support for after-the-fact investigations of security incidents and to meet regulatory and organizational information retention requirements. Additionally an automated cron has been setup to remove indexes that are older then 9 months.
It should be noted that any index can be backed up and exported from a specific period and / or range a time and then backed up to persistent storage in order to comply with security requirements that these logs be kept for at least two years.
Additionally, if required by security requirements for specific requests, the following information may also be added to generated audit logs to provide the full context.